Portainer
Let's launch Portainer Enterprise Edition with three free nodes and unlock the skills necessary to realize the power of containerized apps in your cluster while reducing the operational overhead of deploying them. Pretty awesome right?! 🎉

In this section I will show you how to set up Portainer in a Docker Swarm using Docker Compose and enable it for use with Traefik. Everything will be done from a file.
This section will show you a complete Docker Compose file and the command you need to create the required agent network for Portainer to work in your Docker Swarm cluster.
If you skipped or missed the last section where we configured Traefik, you can check it out at the link below.
What Is Portainer And Why?
Portainer is a container management software to deploy, troubleshoot, and secure applications across cloud, datacenter, and Industrial IoT use cases.
With Portainer we accelerate container adoption in our organization with ease. It reduces operational complexity and addresses the security challenges of running containers in Docker, Swarm, Nomad, and Kubernetes. Awesome! ✌️
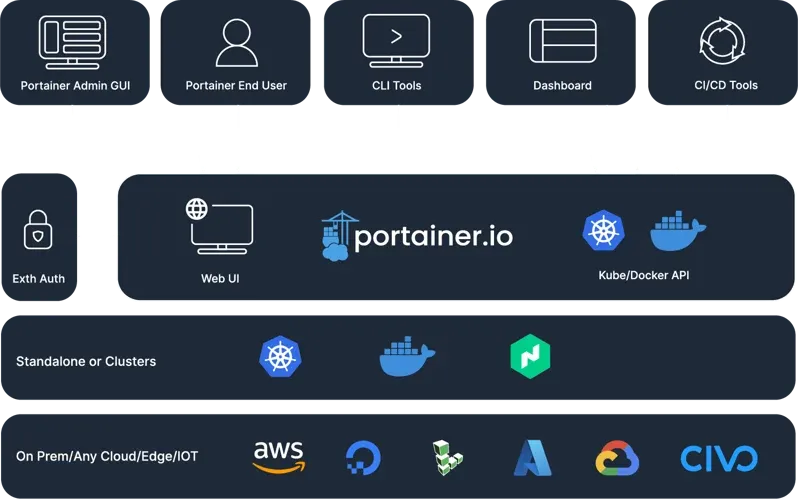
With Portainer we will have an agent on each of our nodes in the cluster, including the leader/manager. They will be the ones with access to Docker Socket and provide Portainer with the required functionality to manage our Docker Swarm.
Make The Folders
Navigate to the /srv/docker/services/ folder and make a new folder named portainer.
mkdir portainer && cd $_That is actually everything we need for the folders to organize Portainer in our cluster. Everything else will be defined in the compose file we will be making in a moment.
Spin Up Portainer BE In Docker Swarm
Portainer has already done a great amount of work in terms of creating a Docker Compose file for spinning up the whole stack required for running Portainer in a Docker Swarm.
However, we still need to create a new agent network for the Portainer agents we will deploy on each of the nodes.
Create The Agent Network
On your leader/manager node, run the following command in your terminal to create a new agent_network.
docker network create -d overlay agent_networkThis will add a new network like the network we created earlier for our proxy.
Create Docker Compose For Portainer
Inside the portainer folder, create a new file named docker-compose.yml and paste the following content inside it.
version: "3.3"
services:
agent:
image: portainer/agent:2.19.4
environment:
AGENT_CLUSTER_ADDR: tasks.agent
AGENT_PORT: 9001
volumes:
- /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock
- /var/lib/docker/volumes:/var/lib/docker/volumes
networks:
- agent_network
deploy:
mode: global
placement:
constraints: [node.platform.os == linux]
portainer:
image: portainer/portainer-ee:2.19.4
command: -H tcp://tasks.agent:9001 --tlsskipverify
networks:
- proxy
- agent_network
volumes:
- /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock
- portainer_data:/data
deploy:
mode: replicated
replicas: 1
placement:
constraints: [node.role == manager]
labels:
# Frontend
traefik.enable: "true"
traefik.docker.network: "proxy"
traefik.http.routers.portainer-frontend.rule: "Host(`portainer.yourdomain.com`)"
traefik.http.routers.portainer-frontend.entrypoints: "https"
traefik.http.routers.portainer-frontend.service: "portainer-frontend"
traefik.http.routers.portainer-frontend.tls.certresolver: "letsEncrypt"
traefik.http.routers.portainer-frontend.tls.options: "modern@file"
traefik.http.routers.portainer-frontend.tls: "true"
traefik.http.services.portainer-frontend.loadbalancer.server.port: 9000
# Edge
traefik.enable: "true"
traefik.docker.network: "proxy"
traefik.http.routers.portainer-edge.rule: "Host(`edge.yourdomain.com`)"
traefik.http.routers.portainer-edge.entrypoints: "https"
traefik.http.routers.portainer-edge.service: "portainer-edge"
traefik.http.routers.portainer-edge.tls.certresolver: "letsEncrypt"
traefik.http.routers.portainer-edge.tls.options: "modern@file"
traefik.http.routers.portainer-edge.tls: "true"
traefik.http.services.portainer-edge.loadbalancer.server.port: 8000
networks:
proxy:
driver: overlay
external: true
agent_network:
driver: overlay
external: true
volumes:
portainer_data:At the time of creating this series, the Docker version from Portainer was 2.19.4. Please check if they have released a new version before deploying this image into your swarm. It can be updated, but there is no reason to deploy old software, right? 😄
Let's break the compose file down. We have two services, let's start with those. The first service is our agents for Portainer.
services:
agent:
image: portainer/agent:2.19.4
environment:
AGENT_CLUSTER_ADDR: tasks.agent
AGENT_PORT: 9001
volumes:
- /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock
- /var/lib/docker/volumes:/var/lib/docker/volumes
networks:
- agent_network
deploy:
mode: global
placement:
constraints: [node.platform.os == linux]This service uses the agent image and has two environment variables. The name of the agent cluster address should be equal to the service name prefixed by "tasks.", when we deploy the agent inside an overlay network. Our service is named agent, hence the name tasks.agent and we will deploy them inside the overlay network agent_network.
We are mounting the docker.sock and /var/lib/docker/volumes paths into the agent for it to communicate with the Docker Daemon and having access to volumes for docker. The network we will attach is our overlay network for the agents and we would like to deploy an agent on each node running Linux as OS.
Now for Portainer 🥳
services:
portainer:
image: portainer/portainer-ee:2.19.4
command: -H tcp://tasks.agent:9001 --tlsskipverify
networks:
- proxy
- agent_network
volumes:
- /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock
- portainer_data:/data
deploy:
mode: replicated
replicas: 1
placement:
constraints: [node.role == manager]
labels:
# Frontend
traefik.enable: "true"
traefik.docker.network: "proxy"
traefik.http.routers.portainer-frontend.rule: "Host(`portainer.yourdomain.com`)"
traefik.http.routers.portainer-frontend.entrypoints: "https"
traefik.http.routers.portainer-frontend.service: "portainer-frontend"
traefik.http.routers.portainer-frontend.tls.certresolver: "letsEncrypt"
traefik.http.routers.portainer-frontend.tls.options: "modern@file"
traefik.http.routers.portainer-frontend.tls: "true"
traefik.http.services.portainer-frontend.loadbalancer.server.port: 9000
# Edge
traefik.enable: "true"
traefik.docker.network: "proxy"
traefik.http.routers.portainer-edge.rule: "Host(`edge.yourdomain.com`)"
traefik.http.routers.portainer-edge.entrypoints: "https"
traefik.http.routers.portainer-edge.service: "portainer-edge"
traefik.http.routers.portainer-edge.tls.certresolver: "letsEncrypt"
traefik.http.routers.portainer-edge.tls.options: "modern@file"
traefik.http.routers.portainer-edge.tls: "true"
traefik.http.services.portainer-edge.loadbalancer.server.port: 8000We will use the Portainer Enterprise Edition image. You will be shown how to obtain a free license for three nodes in a moment. If you want to continue using the Community Edition, simply change the image for Portainer to portainer/portainer-ce:2.19.4.
We are attaching portainer to both the proxy and agent_network in our Docker Swarm. This time we are adding a new volume named portainer_data. This volume will be used to store a database for Portianer along with the config/data files needed for running Portianer.
Finally, we have the deployment section where we tell Docker Compose to deploy this with 1 replica and do it on a manager/leader node. The last section of the deployment is the labels and here we enable traefik and instruct traefik how we would like this service exposed to the public. As you probably have noticed, we have two services exposed (remember to update the domain to your domain and fix the DNS). We are making use of the details we configured in our traefik configuration files earlier to make our lives easier.
Deploy Portainer
With the Docker Compose file in place, let's deploy the stack for portainergets and check if it shows up in Traefik, get's an SSL certificate, and that we can access it from a browser.
Run the following command in the /srv/docker/services/portainer/ folder on your manager/leader node in the cluster.
docker stack deploy -c docker-compose.yml portainerDocker will now pull the image from Docker Hub and deploy the required services in our Docker Swarm. Once that is done, Traefik will pick it up, do its work, and bam you can access it from a browser.
Run the following commands in your console to check if the deployment went well.
docker stack ls
docker service lsYou should get an output like this:
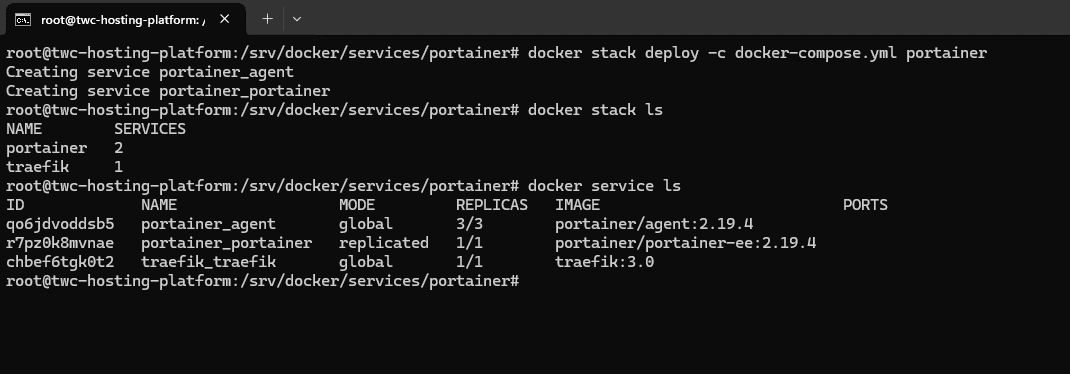
Looks good! Let's check Traefik and see if everything went well.
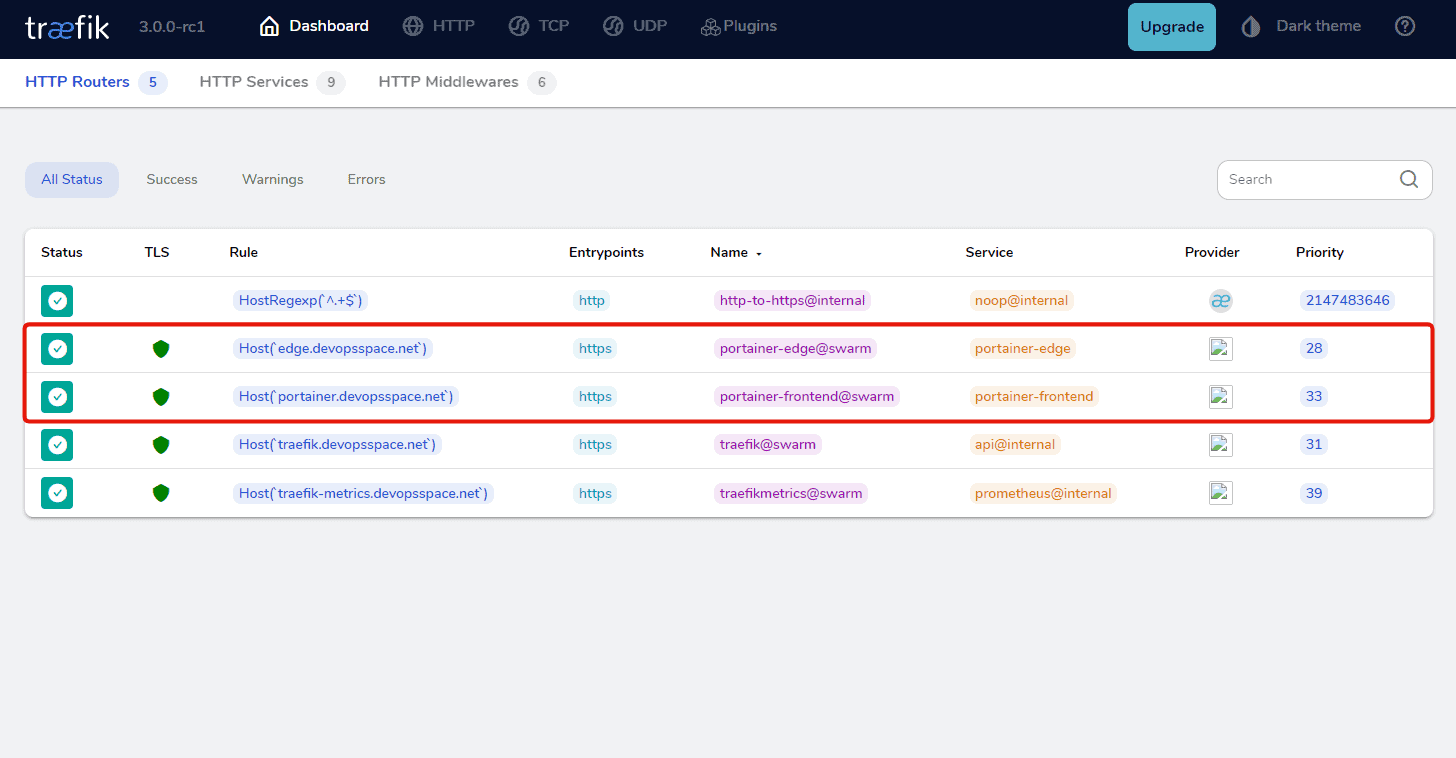
Awesome! Let's try the URL and see what happens. You should see a page where you can create a new account. Go ahead and do that, the details will be stored in a database inside the volume you created for portainer.
You will now be asked to enter a license key if you deployed the service using the EE image.
Get A Portainer Business Edition License For Free
Portainer is very kind 😎 They offer a free Business License for three nodes. The only thing you have to do is sign up on their page and receive a license in your inbox within a minute or two.
When you have filled out the form, you will receive an email like this:
Copy the license and paste it into the form at Portainer where you just created your admin account.

You are now good to go. Sign in and enjoy your Portainer Business Edition deployed on Docker Swarm with Agents. The final result should look like this.
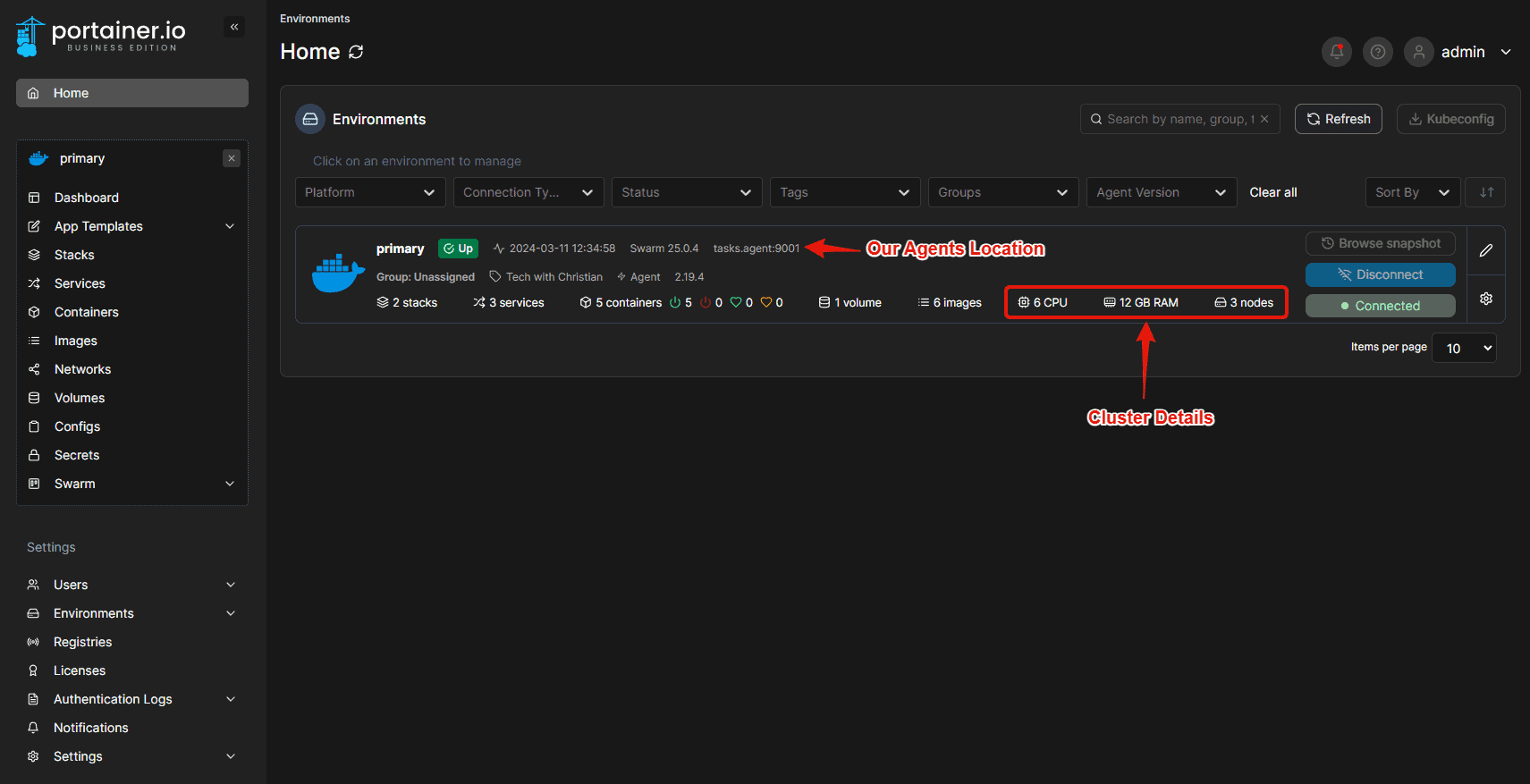
You can now navigate around in Portainer. If you would like to know how to use Portianer. Please check out the official documentation on their website.
Summary
Great job! You have now successfully deployed Portainer into your Docker Swarm with an agent node on all the nodes. You have obtained a license for Portainer and created a new admin account.
Try playing a little with Portainer. Deploy a stack or two, remember to include the labels required for Traefik, and see how awesome this tool is. You can also check out some of the already deployed services and see their consumptions and logs directly in the browser.
In the next section, we will have a look at how to deploy Prometheus in our cluster and configure it to monitor our Traefik service. These metrics will come in handy when we deploy Grafana later. See you in a bit! ✌️

